Yeah, the future of democracy in the US hinges on this case.
"*I don’t often get to use the term gobsmacked, but that is how I was rendered when I saw the film Jurassic Park. I remember the 1993 cinema trip vividly: clutching my popcorn, wide-eyed, as the first dinosaur, a brachiosaurus, ambled across the screen. Walking out with my parents, I jabbered with excitement: “Could we really make dinosaurs real again, Dad? Could we? Could we?”
These memories came flooding back as I read Natasha Bernal’s piece in Wired UK, exploring the world of biobanking animal cells. Bernal answers the question of whether extinct animals could be brought back with a tentative yes — science has long proved that “frozen cells from extinct animals could potentially be used to revive species” — but that is not what biobanking is about. The intention is to increase the diversity of living species, cloning to prevent further loss, rather than to bring back what is already gone. As a species dwindles, so does its genetic pool, and frozen cells from extinct animals could potentially be used to help prevent extreme inbreeding.
Bernal’s case study is Tullis Mason, a chap who sports “three-quarter length shorts” even in a lab coat. Matson runs an artificial insemination company for racehorses from his family’s farm in Shropshire, England. However, on the side, he is also planning to save the animal kingdom by building the biggest biobank of animal cells in Europe. It’s not always a dignified business, with Bernal describing Mason hooking an elephant penis into a device that looks like “a huge condom,” but the science and the ethics her article explores are fascinating. We may not be about to bring dinosaurs back to life, but with help from biobanking, life already on this planet might still find a way.
This is why, back at Matson’s farm, there is a tiny, black, felt-like ear and two bat testicles the size of olive pits on a lab bench. The Seba’s short-tailed bats at Chester Zoo are usually housed in the Fruit Bat Forest, where visitors can feed them as part of a £56 “experience”. Though not currently listed as endangered, with global biodiversity at a tipping point, it’s likely that no species is entirely safe. This bat died of natural causes, but its genetic material will live on.
The first thing that Lucy Morgan, a scientific advisor at Nature’s SAFE, does is shave the ear. “Ears grow to a certain extent throughout our lifetime, so they’re a cell type that’s already wanting to grow and regenerate itself,” she says. “So when choosing a sample that you’re trying to pick to culture in the future, it’s a good one.”
She puts the ear to soak in chlorhexidine to clean it from bacteria and switches on a timer. After two minutes, she transfers it to a petri dish, and starts cutting it into small pieces the size of chocolate chips. Using tweezers, she puts them in cryovials filled with cryopreservant. The tiny testicles will be preserved whole. They couldn’t get any semen out of them – a common problem for animals that are too small to preserve in the traditional manner.
Safely pipetted into a cryovial or straw, an animal’s tissue, semen or ova are deposited into the cryogenic tank, ready to be unfrozen when they may be needed for repopulation programmes in zoos or, if feasible, the wild. In the case of some creatures, whose anatomical challenges do not currently permit artificial insemination using sperm or ova, the samples may stay there for decades. For now, all of Nature’s SAFE’s samples are in one location, but the charity aims to build a backup so that tissue can be split into different places and safeguarded for the future.*"
Upvote for effort
And the dumbest
politics
Welcome to the discussion of US Politics!
Rules:
- Post only links to articles, Title must fairly describe link contents. If your title differs from the site’s, it should only be to add context or be more descriptive. Do not post entire articles in the body or in the comments.
Links must be to the original source, not an aggregator like Google Amp, MSN, or Yahoo.
Example:
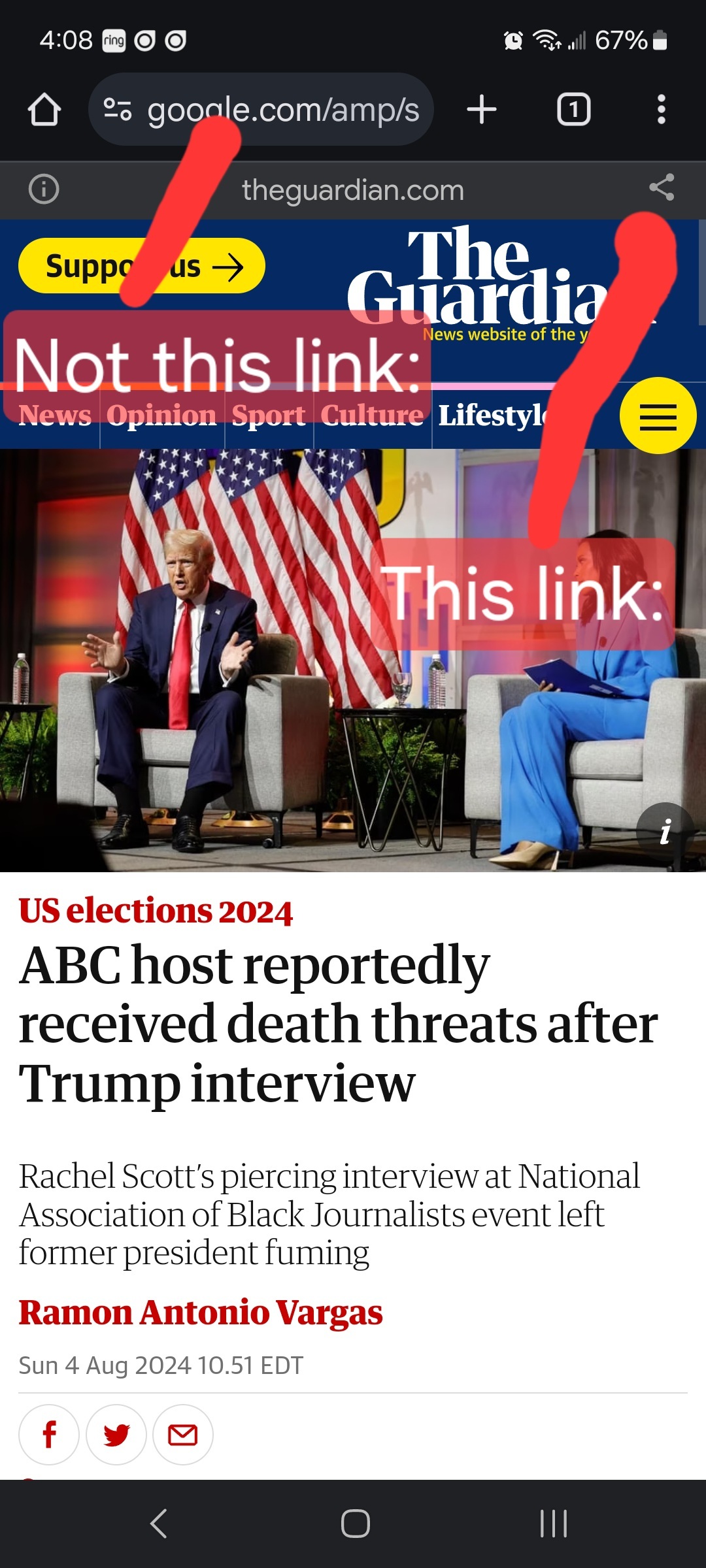
- Articles must be relevant to politics. Links must be to quality and original content. Articles should be worth reading. Clickbait, stub articles, and rehosted or stolen content are not allowed. Check your source for Reliability and Bias here.
- Be civil, No violations of TOS. It’s OK to say the subject of an article is behaving like a (pejorative, pejorative). It’s NOT OK to say another USER is (pejorative). Strong language is fine, just not directed at other members. Engage in good-faith and with respect! This includes accusing another user of being a bot or paid actor. Trolling is uncivil and is grounds for removal and/or a community ban.
- No memes, trolling, or low-effort comments. Reposts, misinformation, off-topic, trolling, or offensive. Similarly, if you see posts along these lines, do not engage. Report them, block them, and live a happier life than they do. We see too many slapfights that boil down to "Mom! He's bugging me!" and "I'm not touching you!" Going forward, slapfights will result in removed comments and temp bans to cool off.
- Vote based on comment quality, not agreement. This community aims to foster discussion; please reward people for putting effort into articulating their viewpoint, even if you disagree with it.
- No hate speech, slurs, celebrating death, advocating violence, or abusive language. This will result in a ban. Usernames containing racist, or inappropriate slurs will be banned without warning
We ask that the users report any comment or post that violate the rules, to use critical thinking when reading, posting or commenting. Users that post off-topic spam, advocate violence, have multiple comments or posts removed, weaponize reports or violate the code of conduct will be banned.
All posts and comments will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis. This means that some content that violates the rules may be allowed, while other content that does not violate the rules may be removed. The moderators retain the right to remove any content and ban users.
That's all the rules!
Civic Links
• Congressional Awards Program
• Library of Congress Legislative Resources
• U.S. House of Representatives
Partnered Communities:
• News