Hi,
I have a Pi-Hole set up on my home network, which I access from anywhere through a SWAG reverse proxy at https://pihole.mydomain.org. I have set up a local DNS record in Pi-Hole to point mydomain.org to the local IP of the SWAG server.
Access from anywhere (local or not) works well. It's just that when I am accessing some services (including the Pi-Hole) from my desktop through the reverse proxy via the DNS record (i.e. on the LAN), the Pi-Hole log gets completely spammed with requests like in the attached image. To be clear, I cropped the image, but it is pages and pages of the same. This is also the case for e.g. the qBittorrent Docker container I have set-up. So I guess it's for 'live' pages which update their stats continuously, which makes sense. But the Pi-Hole log is unusable in this state. This does not occur when I am accessing the services externally, through the same reverse proxy, or when I access them locally with their local IP.
The thing is, I have already selected Never forward non-FQDN A and AAAA queries in the Pi-Hole settings. I also have Never forward reverse lookups for private IP ranges, Use DNSSEC, and Allow only local requests, but they seem less relevant.
The Pi-Hole, SWAG server, and PC I am accessing them from are three different machines on my LAN.
Any way to filter out just those queries? I obviously want to preserve all the other legitimate queries coming from my desktop.
EDIT: Thanks for the responses. Unfortunately the problem persists, but I discovered something new. This only happens when accessing the page from Firefox desktop; not another desktop browser, and not Firefox Android. So actually it seems to be a Firefox problem, not a Pi-Hole one. I thought this might have something to do with Firefox's DNS-over-HTTPS, so I tried both adding an exception for my domain name, and disabling it altogether, but that didn't solve it..
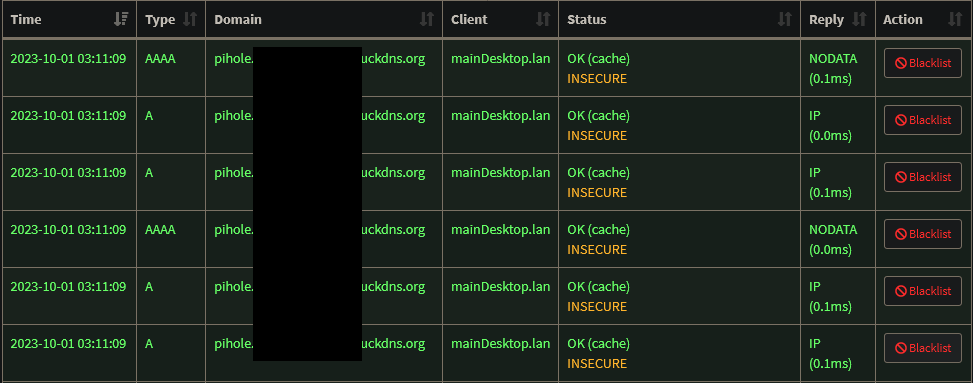
Could this be because you've set the forwarded address to be insecure in the reverse proxy essentially doing SSL termination at the reverse proxy? To test this theory, set the destination local address to also use https not just http