39
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
this post was submitted on 10 Sep 2024
39 points (93.3% liked)
[Dormant] moved to !space@mander.xyz
11059 readers
1 users here now
This community is dormant, please find us at !space@mander.xyz
You can find the original sidebar contents below:
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
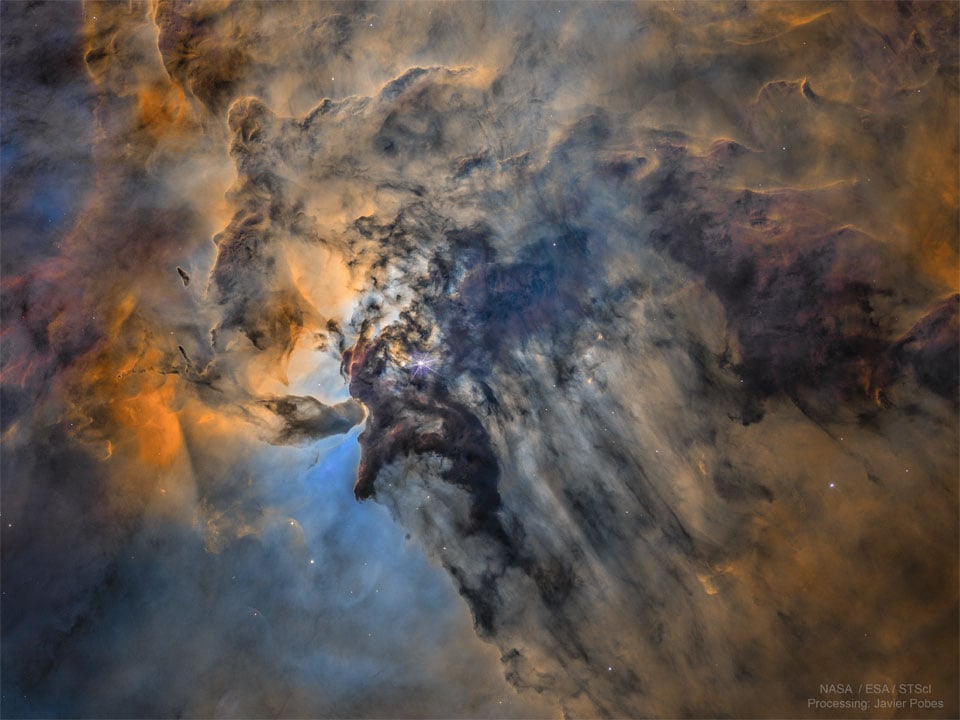 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
Considering some data centers basically need a power plant to run, the amount of solar panels needed would be insane. Plus, unless you keep the data center between the planet and the sun, you still have shade.
There is such a thing as Sun-synchronous polar orbits (an example).
Neat
The way I understand is that they would use a sun-synchronous orbit, more specifically a dawn/dusk orbit, which places the satellite over the terminator between day and night meaning it always directly sees the sun. But yes, it would need an insane number of solar panels. What's more, data centers don't just need power, they also need cooling. So there would also need to be an insane amount of radiators (in space it's very hard to get rid of heat).
All in all the only advantage I can see is not much of an advantage, if at all, especially compared to all the drawbacks.